How Structural Thermal Breaks Improve Energy Performance
In today’s construction landscape, balancing energy efficiency with structural stability is critical. The industry continually seeks intelligent solutions to improve building envelope performance and structural thermal breaks have emerged as a leading technology in this area.
These solutions can help to reduce heat transfer and thermal bridging, working towards better energy efficiency, minimal environmental impact and improved comfort for occupants and visitors. Different types of thermal breaks are designed for various applications to combat thermal bridging, reducing the energy flow across various construction connections.
Material-based breaks
These combine high insulation performance with strong compressive strength, suitable for slabs, roofs and other load-bearing applications. Armatherm™ 500 is a thermoset polyurethane available in multiple densities, offering a range of compressive strengths and R-values.
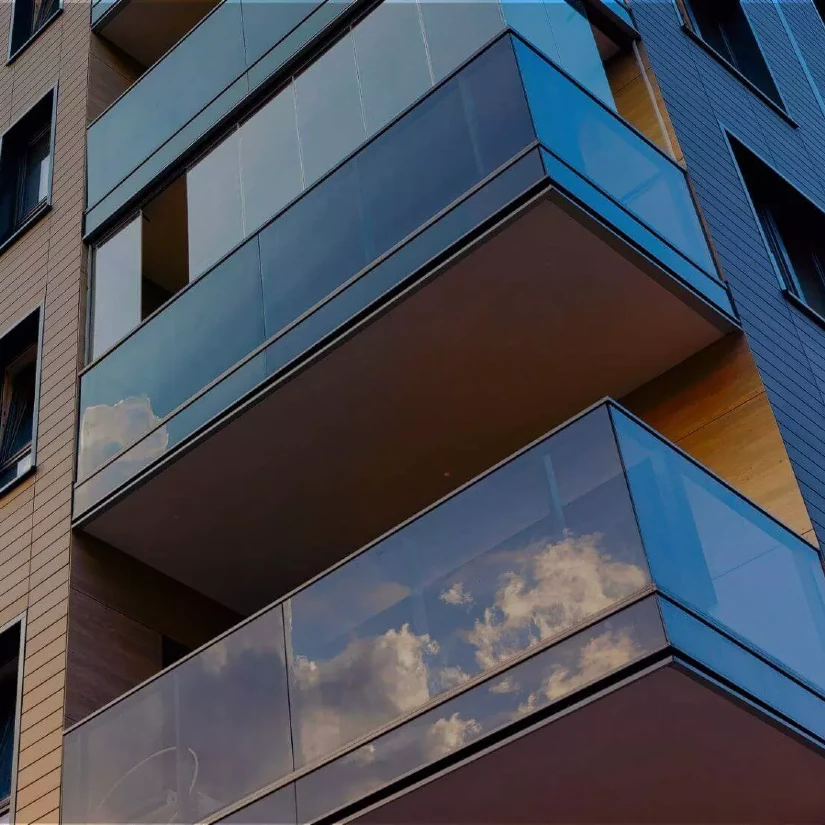
Lightweight, corrosion-resistant and easy to install, reinforced fiberglass thermal breaks are commonly used in façades and balcony connections. The ArmaGirt™ Z Girt is an example, improving R-values while reducing heat loss.
Phenolic foam provides low smoke emission and fire-resistant properties, ideal for fire-rated walls and partitions. Armatherm™ FRR combines high mechanical strength with fire resistance, making it suitable for structural steel and façade applications.
Isolated connections
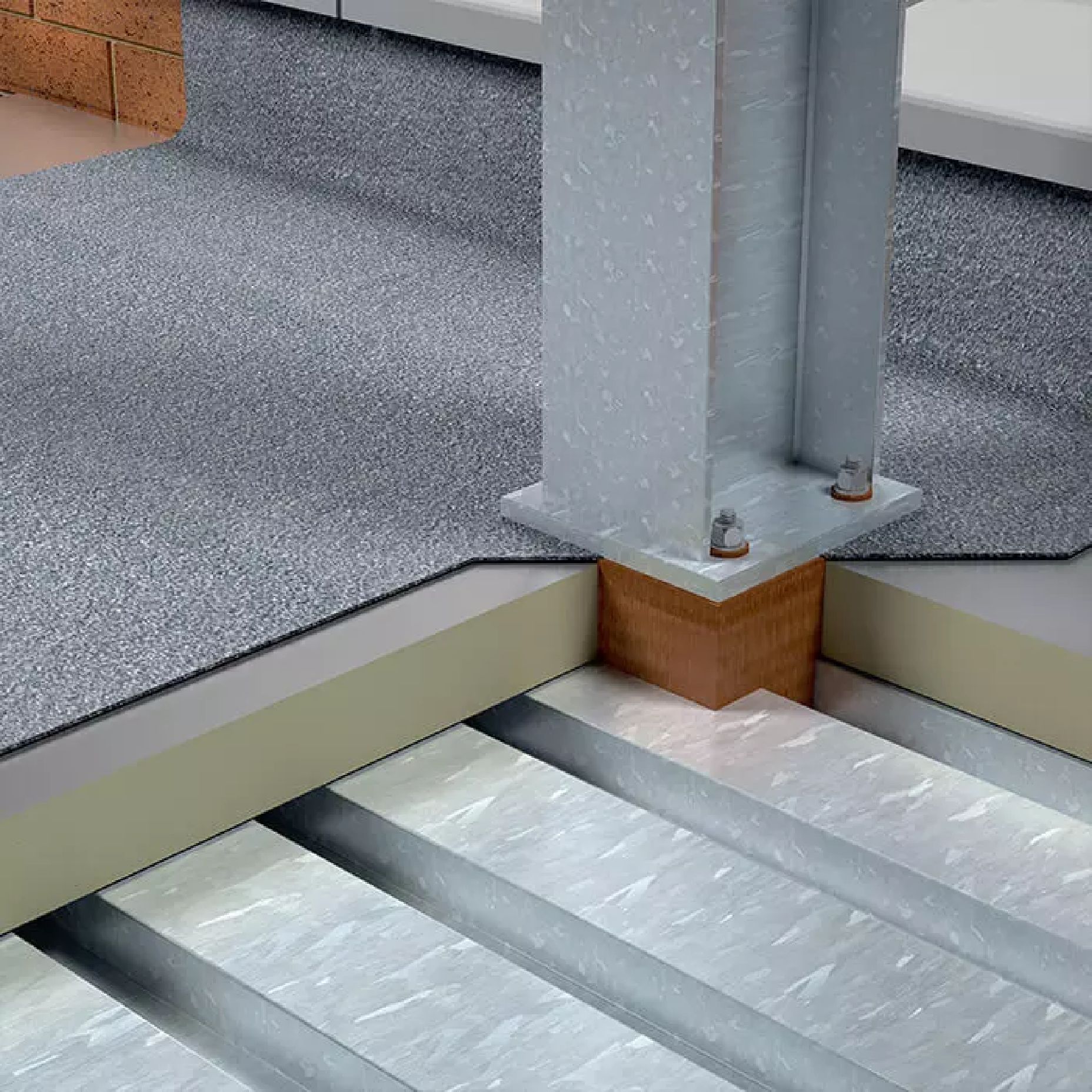
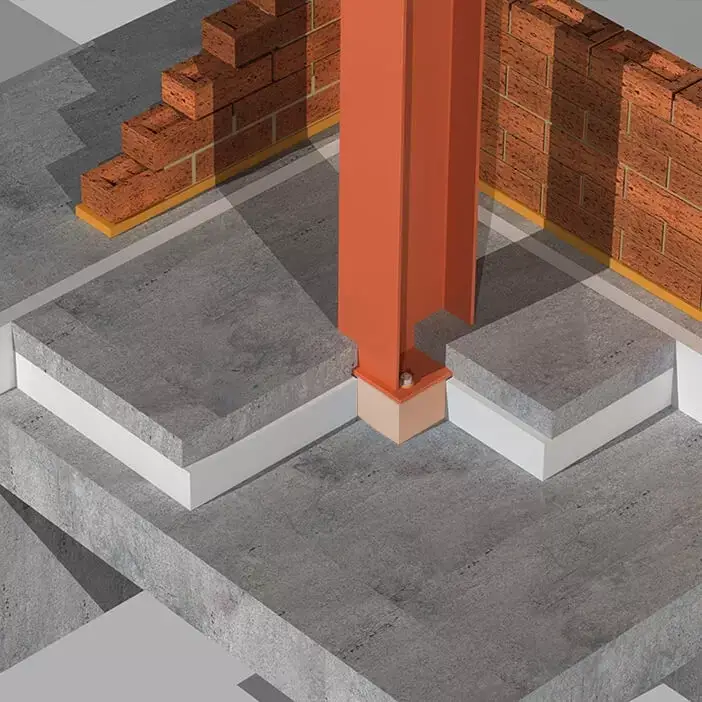
Steel-to-steel isolation is needed wherever insulating materials are placed between steel members such as beams or columns. This approach is common in both commercial and industrial projects where steel framing is used.
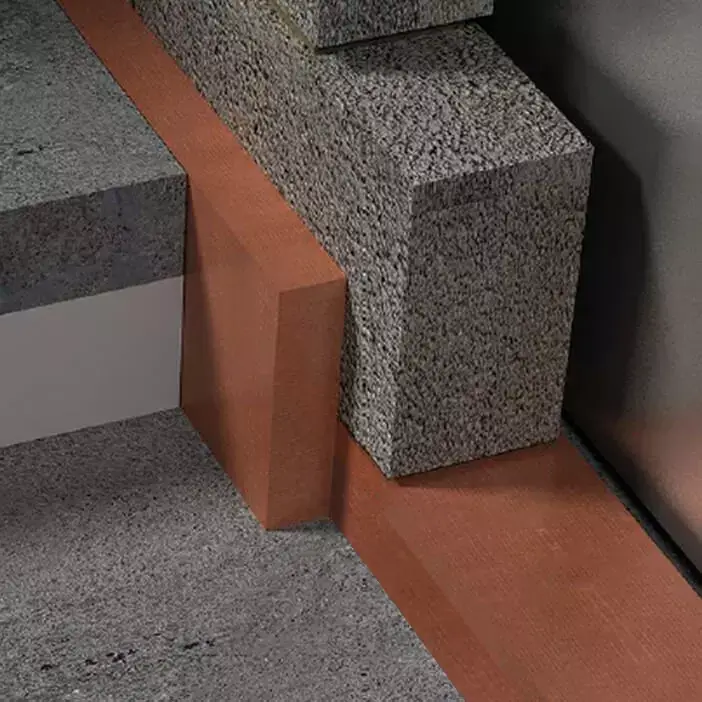
For reinforced concrete construction, concrete-to-concrete isolators or disconnectors are applied to divide elements like slabs and walls. Given the heavy load demands of concrete, a high load-bearing thermal break provides the most effective solution.

Hybrid thermal breaks
Hybrid thermal breaks are innovative components that merge the benefits of material-based systems with isolated connection solutions, delivering both structural support and improved thermal resistance. Designed to combat thermal bridging more efficiently, these systems help maximize a building’s overall energy performance. Their adaptability and effectiveness have made them increasingly popular across the construction sector. A typical hybrid solution pairs insulating material with isolators to limit heat transfer. The ArmaGirt™ Z Girt illustrates this approach, not only reducing thermal loss through the envelope but also boosting the wall assembly’s effective R-value.
One of the key benefits of using structural thermal breaks throughout a project is the boost they provide to a building’s overall energy performance. By limiting heat transfer and reducing thermal bridges, these components help maintain stable indoor temperatures. This reduces reliance on energy-intensive heating and cooling systems, cutting utility costs and lowering overall consumption. Buildings equipped with thermal breaks stay comfortable for longer periods, requiring less frequent operation of HVAC systems.
Lower energy use directly translates into savings for owners and occupants alike. In colder seasons, less heat escapes; in warmer months, less heat enters. This ensures consistent performance and lower operating costs year-round.
Condensation is another challenge that thermal breaks help address. By keeping the interior surfaces of building elements warmer, they minimize cold spots where moisture can accumulate. This lowers the risk of condensation, mould growth, and material deterioration—resulting in a healthier, more durable indoor environment.
Thermal breaks also improve comfort by eliminating cold zones and temperature fluctuations inside the building. Occupants enjoy a steadier indoor climate, enhancing satisfaction and usability of the space.
Beyond comfort, structural thermal breaks protect the building itself. By reducing thermal stress and moisture-related wear, they extend the life of structural elements and cut down on costly repairs or maintenance over time.
From a sustainability perspective, thermal breaks align with green building initiatives and energy codes. They contribute toward certifications like LEED and Passive House, helping projects meet strict efficiency standards without the need for major retrofits later.
Flexibility is another advantage. Thermal breaks are available in many forms and can be tailored to suit different connection types, structural layouts, and architectural designs. This makes integration seamless across a wide range of projects.
With many modern building codes requiring attention to thermal bridging, incorporating thermal breaks ensures compliance while supporting the construction industry’s shift toward sustainable, responsible practices. By adopting these solutions, designers and builders not only improve energy performance but also advance a culture of long-term environmental stewardship.
By embracing the most innovative energy solutions in the market, the construction industry fosters a culture of sustainability and responsible building practices. This cultural shift will lead to a more sustainable and environmentally conscious future for the building industry.
Maintain thermal continuity between cladding and the main structure.
Reduce heat loss and gain at roof junctions, contributing to improved thermal performance and overall efficiency.
Prevent thermal bridging in exterior protrusions. Thermal breaks in balcony connections help reduce any heat transfer from occurring, preventing discomfort for occupants or visitors and enhancing the overall energy efficiency.
Maintain a continuous thermal barrier around windows, doors and slab edges. This prevents localized heat loss or gain, creating a more comfortable indoor living environment and reducing heat and cooling costs.
Both these connections can act as thermal bridges if not adequately addressed. Structural thermal breaks in these areas minimize heat transfer and maintain the thermal integrity of the building envelope.
Advancements in modern science have driven the creation and production of next-generation materials designed specifically for structural thermal breaks.
The construction industry has also seen major progress through prefabrication, and this trend extends to thermal break technology. Companies like Armatherm supply prefabricated thermal break components that are precision-cut, pre-drilled, and ready for immediate installation—helping projects save both labor time and costs. For added flexibility, thermal break materials are also available in sheet form for on-site cutting.
Another key innovation is the ability to integrate load-bearing functionality into thermal break systems. Many suppliers now provide fully customizable solutions, allowing architects and engineers to specify exact dimensions and thicknesses to suit project-specific needs. By working directly with manufacturers, engineers can ensure the thermal break aligns seamlessly with unique structural requirements, enhancing both fit and performance. This adaptability makes it easier to incorporate breaks into building features such as façades and roof assemblies.
Today’s thermal breaks not only deliver effective thermal separation but also enable load transfer between structural elements. This dual function is critical for maintaining structural integrity while significantly reducing thermal bridging. Such solutions are particularly valuable in applications like balconies and façades, where energy efficiency and stability must work hand in hand. Beyond boosting performance, this approach also simplifies the design process and maximizes material efficiency.
Equally transformative is the rise of continuous insulation systems, which have become a cornerstone in combating thermal bridging. By providing uninterrupted insulation across the full building envelope, they establish a consistent barrier against heat transfer. From masonry walls to curtain wall façades, continuous insulation enhances energy efficiency by minimizing unwanted heat loss or gain.
When combined with complementary solutions such as custom thermal break pads and advanced insulation materials – continuous insulation creates a high-performance thermal envelope. These systems not only deliver superior efficiency but also meet or exceed the toughest energy codes, regulations, and certification standards.

What part do structural thermal breaks play in creating a sustainable future for construction?
The role of structural thermal breaks in shaping a more sustainable construction industry is impossible to overlook. As the global focus on reducing carbon emissions and minimizing ecological impact intensifies, these advanced components are proving essential for driving energy-efficient and environmentally conscious building practices. By reducing thermal bridging, improving energy performance, and supporting compliance with green building standards, thermal breaks help create structures that are both sustainable and resilient. Beyond lowering energy consumption, they also foster healthier indoor environments while lessening the overall impact on the planet – benefits that are both immediate and long-lasting.
For architects, engineers, and contractors, gaining a deeper understanding of innovations like structural thermal breaks is a vital step toward building responsibly for the future. Their adoption represents a fundamental change in the industry, one that aligns environmental responsibility with economic efficiency. As sustainable design continues to gain momentum, structural thermal breaks are positioned to become a standard feature in modern construction, helping deliver greener, more energy-conscious, and forward-looking buildings.
To explore how Armatherm’s thermal break products can improve your project’s efficiency and sustainability, reach out to the Armatherm team through the details provided on our contact page.